What Color Is The Sun? Unraveling A Cosmic Mystery
Have you ever stopped to truly think about the sun’s color? For many of us, the sun is that big, bright, yellow orb hanging in the sky, a rather familiar sight. This idea, you know, it’s been with us since childhood drawings, a common way we picture our star. Yet, what if that common picture isn't quite the full story, or even the most accurate one? It's a question that, frankly, sparks a bit of curiosity, making us wonder about the actual nature of the light reaching us.
The truth about the sun's color, actually, is a little more complex and, in some respects, far more fascinating than a simple crayon drawing might suggest. It involves the very light the sun produces, how it travels through space, and then, crucially, how it interacts with our planet's atmosphere before it ever reaches our eyes. So, what we perceive often isn't the whole picture, but rather, a filtered version, a bit like looking through a colored lens.
This journey of sunlight, from its fiery surface to our daily view, reveals some truly remarkable science. Understanding it can change how you look at the sky, really, and how you think about light itself. It's about peeling back the layers of common perception to discover the scientific reality, a process that, as a matter of fact, can be quite eye-opening.
- Bianca Grammys Outfit No Blur
- How Many 0 For Billion
- How Tall Is Benson Boone
- Meaning Of Am Pm In Time
- Jayshree Gaikwad Web Series
Table of Contents
- The Sun's True Hue: A Cosmic White
- Why Our Sky Looks Blue and the Sun Changes Color
- Sunlight's Reach: More Than Just Color
- Addressing Common Questions About the Sun's Color
- Bringing It All Together
The Sun's True Hue: A Cosmic White
When we talk about what color is the sun, the visible wavelength of light coming from it is, actually, white. This might sound surprising if you've always imagined a yellow sun, but it's a scientific fact. Our star emits light across the entire visible spectrum, meaning it gives off all the colors we can see, and when all those colors mix together, our eyes perceive them as white. It’s a pretty neat trick of physics, really.
You can see this principle at work when light gets separated, like what happens with a prism. A prism takes that seemingly plain white light and, as a matter of fact, spreads it out into its individual components: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet. This is precisely the same process that creates a rainbow after a rain shower, a beautiful display of the sun's full color range, you know, broken apart for us to enjoy.
So, the sun itself, in a way, is a source of pure, unadulterated white light. It's only when this light begins its journey through our planet's atmosphere that things start to look a little different to us. The atmosphere, it turns out, acts like a very complex filter, changing how we experience that brilliant white light. This is, arguably, one of the biggest reasons for the common misunderstanding about the sun’s actual color.
- Cast Of Kpop Demon Hunters
- 1 0 6 And Park
- High Potential Season 2
- Red Crab Juicy Seafood
- How To Craft A Saddle In Minecraft
Learning these kinds of scientific truths, you know, really highlights the value of observation and documentation. Adam Savage, everyone’s favorite mythbuster, once said, "the difference between screwing around and science is writing it down!" That's so true, Adam, so true. It emphasizes how important it is to record our findings, even when they challenge what we thought we knew, making sure we have clear evidence for our understanding.
Why Our Sky Looks Blue and the Sun Changes Color
The reason the sun often appears yellow, orange, or even red to us here on Earth has everything to do with our atmosphere. Simply put, the particles in the atmosphere and the light from the sun are what makes the sun seem blue, or rather, makes the *sky* seem blue. This effect is called Rayleigh scattering, and it's a pretty big deal for how we see our world, actually.
Blue light waves are shorter and scatter more easily than other colors when they hit the tiny molecules of nitrogen and oxygen in our air. This scattering means that blue light gets spread out across the sky, making the entire dome above us appear blue. Meanwhile, the longer wavelengths of light, like red and yellow, travel more directly through the atmosphere, so they are the colors we typically see when we look towards the sun, especially when it's high up, you know.
As the sun gets lower in the sky, during sunrise or sunset, its light has to travel through a much thicker layer of atmosphere. This longer path means even more of the blue light gets scattered away, and a lot of the green and yellow light does too. What's left, then, is mostly the red and orange light, which is why we get those truly stunning, very colorful displays at dawn and dusk. It’s a beautiful demonstration of physics at work, really, playing out every single day.
So, atmosphere and light make a blue sky, and they also, in a way, paint the sun in different hues depending on the time of day and how much air its light has to pass through. It’s a constant, dynamic interaction that, quite frankly, shapes our visual experience of the sun and the sky. This interaction is, basically, why the sun appears to shift its colors, even though its light is always white at its source.
Sunlight's Reach: More Than Just Color
Understanding what color is the sun also means appreciating the broader impact of its light, far beyond just what we see. Sunlight, you know, influences so many aspects of our lives and the natural world, from our own bodies to the plants that grow around us. It's a truly powerful force, one that we interact with every single day, often without even realizing the full extent of its effects.
The Science of Skin and Sunlight
Our skin, for instance, is constantly responding to sunlight. Skin can be considered the plastic wrap of the human body, keeping out bacteria and locking in freshness. It protects your organs from germs, regulates body temperature, and, in fact, does so much more. This protective layer, however, is also deeply affected by the sun's rays, sometimes in ways that change its appearance.
Hyperpigmentation is a darkening of the skin or nail tissue that is, on its own, usually harmless. This effect occurs due to an excess of melanin, often from sun exposure. Melanin, you see, is the natural pigment that gives color to our skin, hair, and eyes, and its production increases as a way to shield our cells from UV radiation. So, the sun, in a way, triggers this natural defense mechanism, changing skin tone.
On the other side of the spectrum, albinism is a genetic condition characterized by little to no melanin in the skin, eyes, and hair. The majority of children born with this condition have parents with normal eye and hair color, which is pretty interesting. For individuals with albinism, sun exposure presents a much greater risk, as their bodies lack that natural melanin shield, making protection from the sun even more important.
The Good and Bad of Sunlight
For decades, medical communities have warned people about the dangers of too much sun exposure. Unfortunately, doctors still diagnose more than five million new cases of non-melanoma skin cancer each year, which is a really sobering statistic. It just goes to show how vital it is to protect ourselves from those powerful rays, even though we need some sunlight for our health.
Blue light, which sunlight naturally radiates, is a prime example of how harmful too much of a good thing can be. Our bodies need this blue light during the day to regulate our sleep cycles and boost our mood, which is pretty cool. However, after the sun sets, artificial lights continue to emit blue light, potentially disrupting our natural rhythms and, frankly, causing some eye strain.
Even if you don't have an allergy, the sun can affect your tattoo, and individuals who live in sunny areas should take steps to protect their artwork. Sun exposure can cause the colors to fade and the lines to blur over time, basically damaging the tattoo's appearance. So, keeping that ink covered or well-sunscreened is a pretty smart move for its longevity.
Sunlight and the Green World
Sunlight also plays a starring role in the vibrant life of our planet, especially when it comes to plants. Adding plants to your interior space not only adds ambiance, but it can also help purify your home or office air quality, which is a nice bonus. These green friends rely on sunlight for photosynthesis, turning that light energy into the fuel they need to grow and thrive.
If you love plants that add loads of color to your landscape or outdoor living area, the mandevilla or rock trumpet is the perfect addition. These plants, you know, just soak up the sun and reward us with their beautiful, bright blooms. They are a wonderful example of how sunlight directly contributes to the visual appeal of our surroundings, making everything feel a bit more alive.
Many gardens lose their color once the summer heat kicks in, which can be a little disheartening. Choosing hardy bloomers that can handle the heat and full sun will keep your green spaces looking bright and beautiful, even during the hottest months. It’s all about selecting the right plants that, basically, thrive under the sun’s intense gaze, ensuring continuous bursts of color. You can learn more about gardening tips on our site, for instance.
Addressing Common Questions About the Sun's Color
FAQ: Is the sun truly white, even though it often looks yellow?
Yes, actually, the sun emits light across the entire visible spectrum, which our eyes perceive as white when all those colors combine. The yellow appearance we often see is a result of Earth's atmosphere scattering blue light away, leaving more of the yellow, orange, and red light to reach our eyes. So, it's a trick of our atmosphere, in a way.
FAQ: Why does the sky look blue if the sun's light is white?
The sky looks blue because of how sunlight interacts with the gases in our atmosphere. Blue light waves are shorter and scatter much more easily than other colors when they hit tiny air molecules. This scattered blue light spreads across the sky, making it appear blue, while the other colors travel more directly towards us, which is pretty interesting.
FAQ: Does the sun's color change during sunrise and sunset?
The sun's actual color doesn't change, but its apparent color certainly does during sunrise and sunset. When the sun is low on the horizon, its light has to travel through a much greater amount of atmosphere. This causes even more blue, green, and yellow light to scatter away, leaving mostly red and orange light to reach our eyes, creating those beautiful, warm hues, you know.
Bringing It All Together
So, when we ask what color is the sun, the simple, scientific answer is white. This brilliant white light, however, becomes a vibrant spectrum of colors as it interacts with our planet’s atmosphere, painting our skies blue and giving us those breathtaking sunrises and sunsets. It’s a wonderful example of how science helps us see the world, really, with greater clarity and appreciation.
Understanding this helps us appreciate the intricate dance between light and matter, a dance that affects everything from the pigments in our skin to the growth of a mandevilla plant. The sun's influence is, basically, everywhere, shaping our visual experiences and our very well-being. It's a truly powerful and constant presence in our lives, one that deserves our thoughtful attention.
Next time you look up at the sky, take a moment to consider the journey of that sunlight, from a pure white source to the colors you see. It’s a pretty cool thought, actually, and it might just make you look at the world around you with a fresh sense of wonder. To learn more about the sun and its properties, you might want to check out a reputable science website, and don't forget to explore other fascinating science topics right here.
- Kevin Leonardo Nair Video
- Cronología De Inter Milan Contra Fc Barcelona
- How To Make An Ender Chest
- Jason Luv Eva Elfie
- Despacito Lyrics English Song

Sun Images
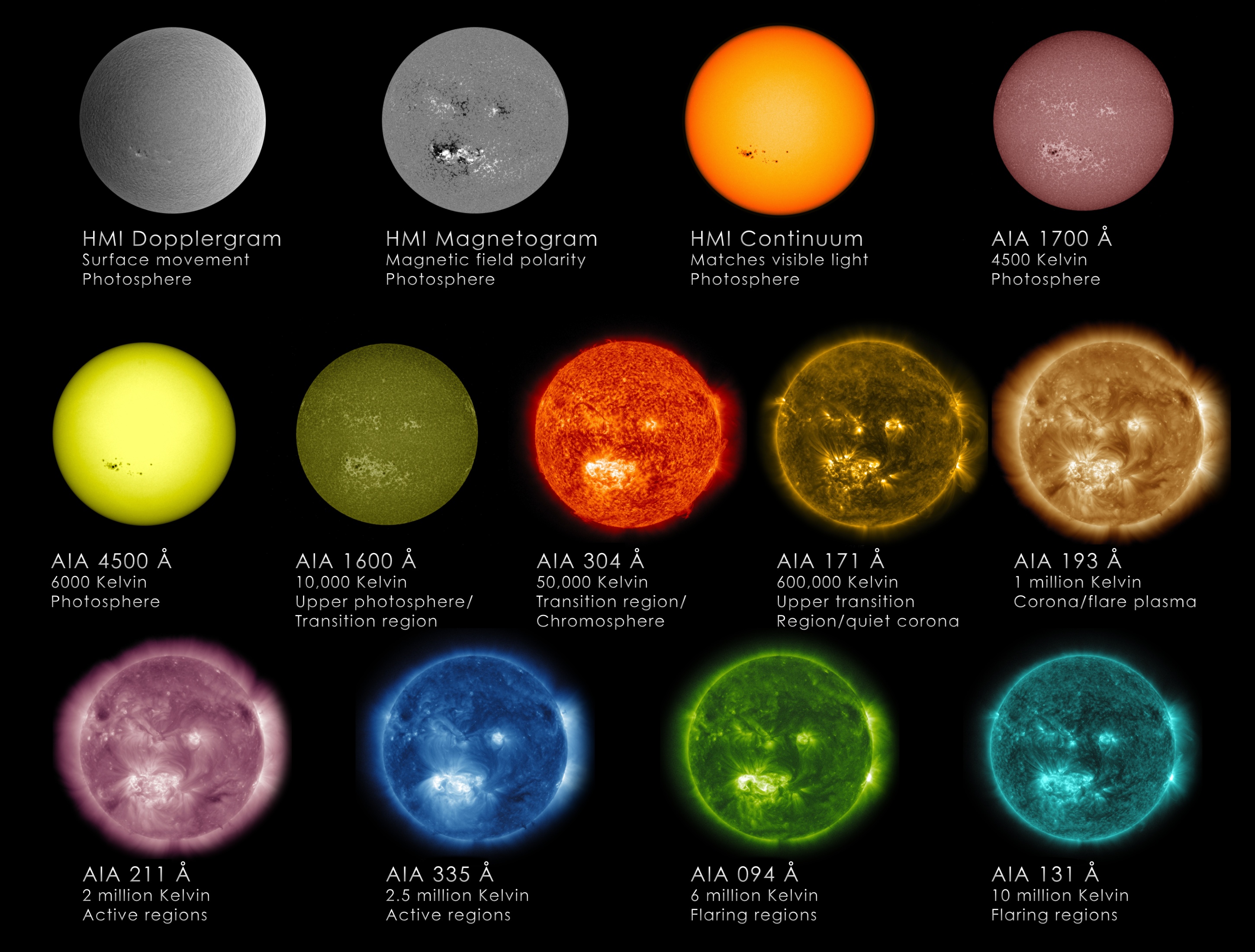
Why does NASA observe the sun in different colors? | The Kid Should See
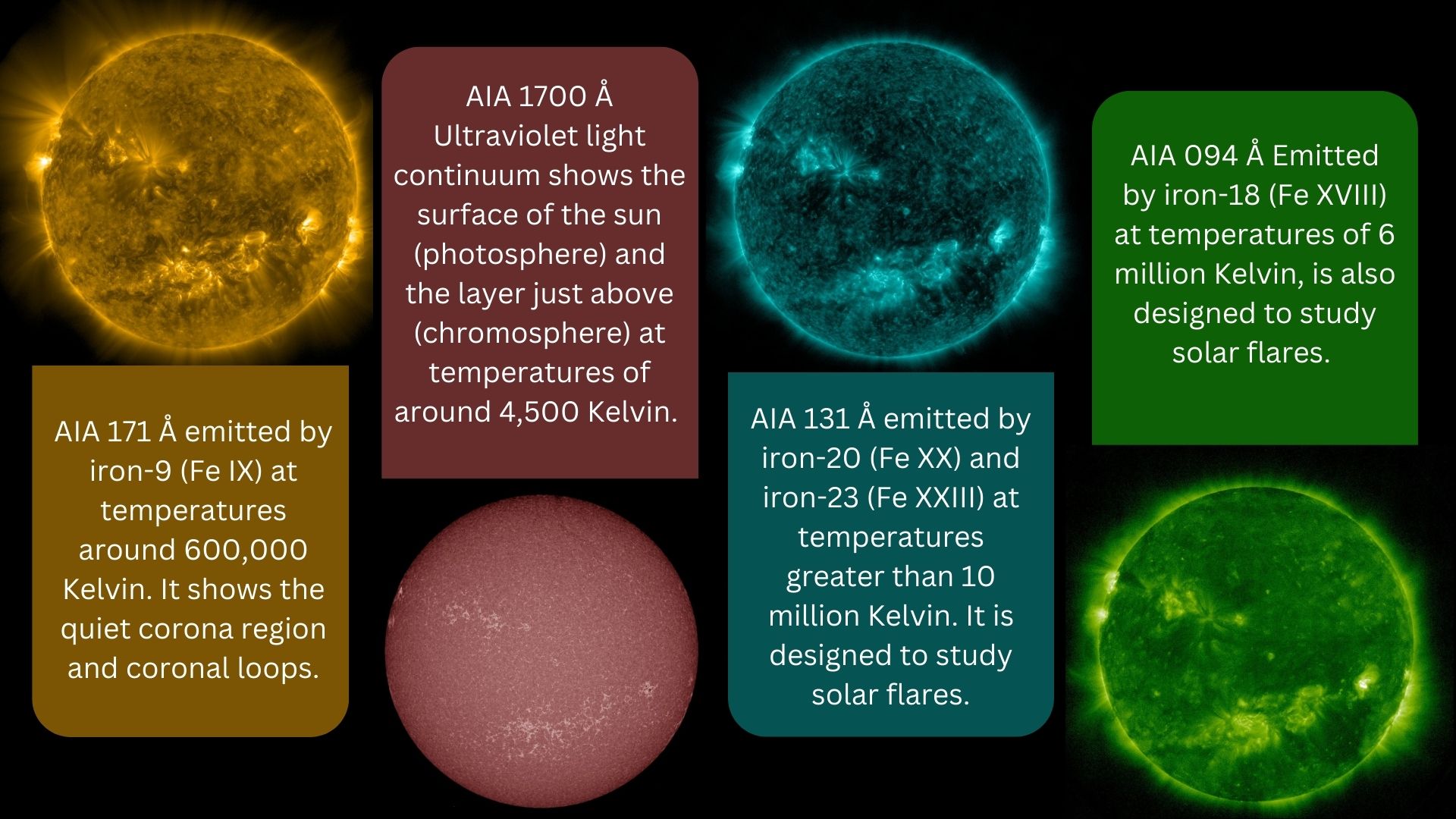
What color is the sun? | Space